?
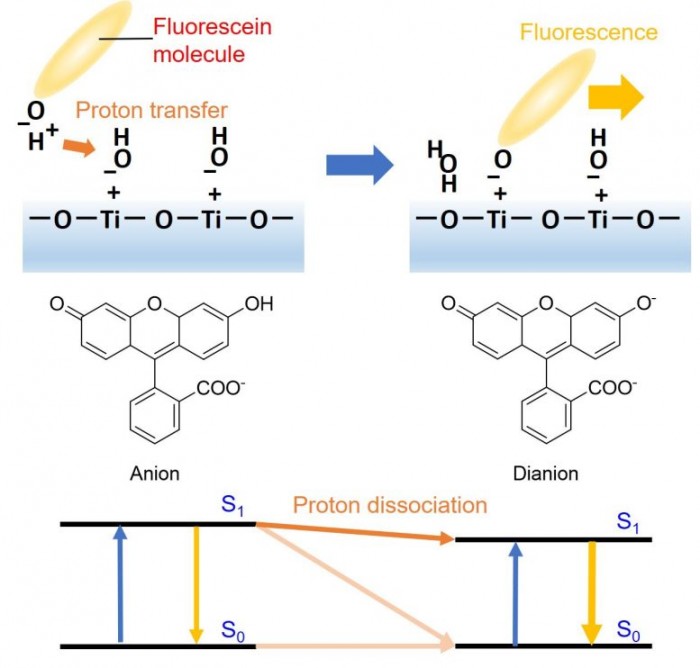
? ? ? In the process of UV irradiation, the temporal changes of the chemical state of titanium dioxide surface can not be observed by conventional methods such as Fourier transform infrared absorption spectroscopy (FTIR) or Raman spectroscopy. Therefore, a team led by Hiromasa nishikiori of rism, Xinzhou University, has observed this reaction by time-resolved fluorescence spectrometry.
? ? ? The team noted that the monoanion of fluorescein was converted into a divalent anion, and that protons were transferred from the fluorescein dye to the surface of titanium dioxide "in the excited state" during ultraviolet irradiation, which was not previously determined by transient absorption spectroscopy.
?
Fluorescein is a kind of organic dye sensitive to light and acidity / alkalinity, which is adsorbed on the surface of titanium dioxide as a probe molecule. The team used femtosecond pulsed laser for time-resolved surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectroscopy. Using femtosecond pulsed laser SPR spectroscopy, the team was able to observe the proton transfer process of dye to the surface of titanium dioxide indirectly, and demonstrated the formation of basic hydroxyl groups.
?
? ? ? ? The observation of UV irradiation time showed that the surface became more alkaline and OH group on the surface of titanium dioxide received protons from fluorescein single anion. It is a very effective method to use organic dyes sensitive to light and acidity / alkalinity to observe the small photoinduced behavior (proton transfer process) on solid surface in a very short time.
? ? ? ? The ratio of binary ions to unit ions of fluorescein was observed by SPR spectroscopy. Professor nishikiori hopes that through the establishment of this simple method, researchers can observe and evaluate the photocatalytic activity, and continue to contribute to the development of photocatalytic water separation for hydrogen production.
? ??

 ?
?